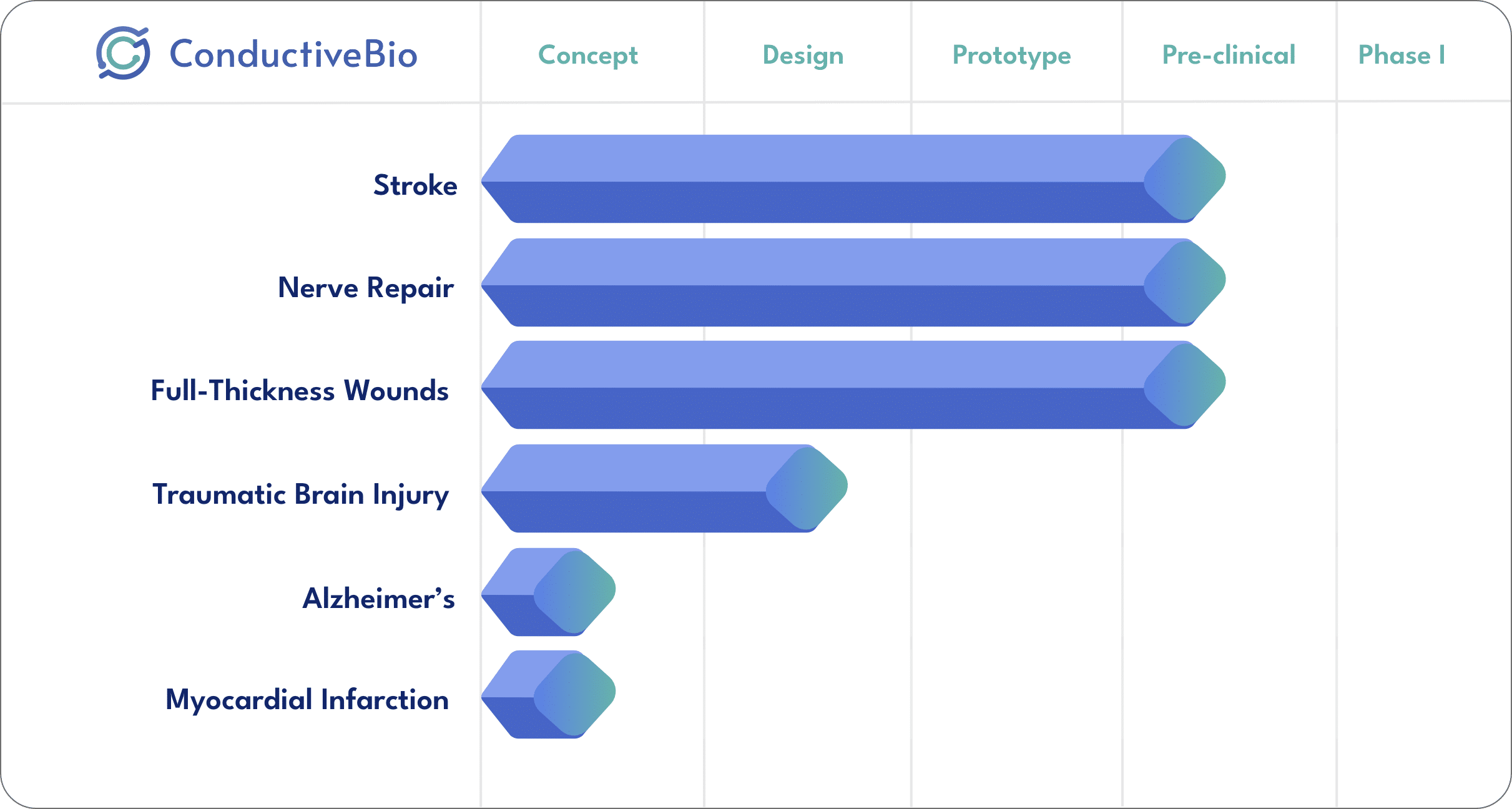
Stroke
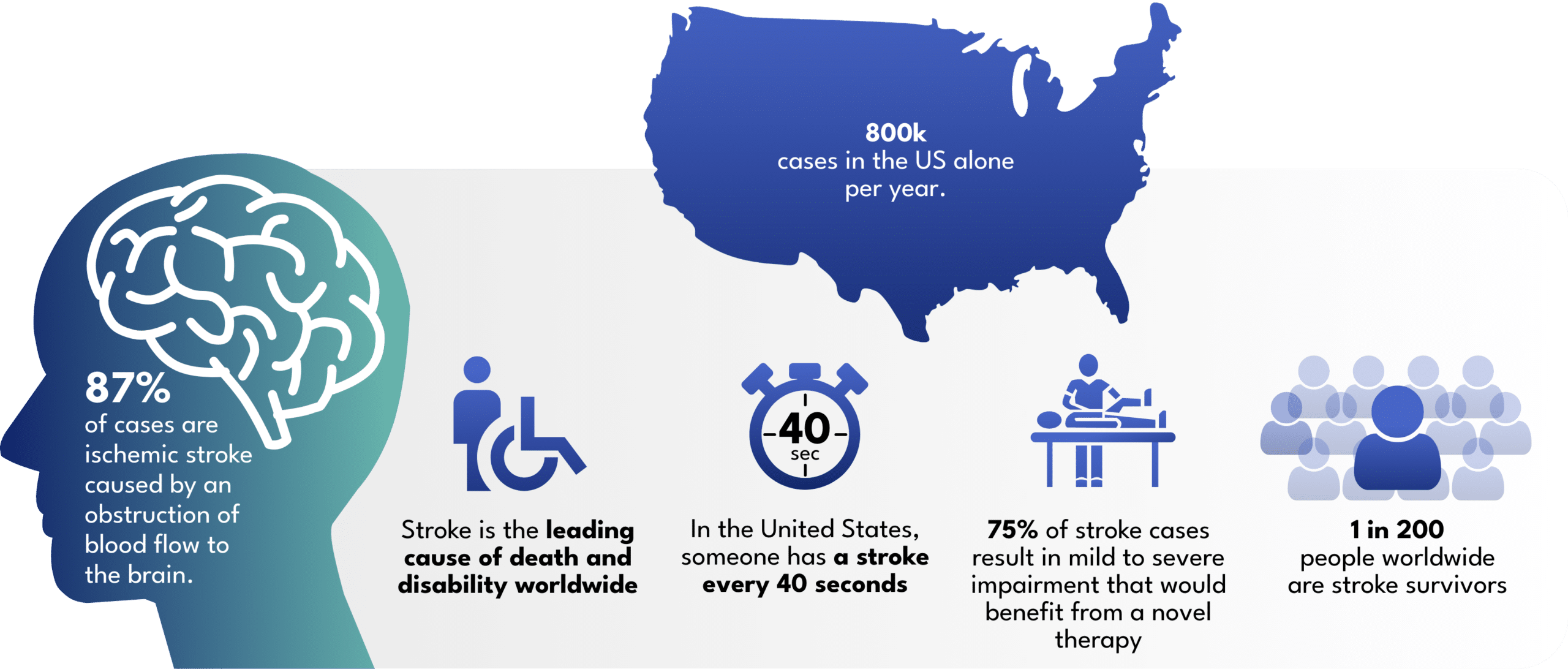
Stroke afflicts patients with varying degrees of impairment, necessitating extensive rehabilitation spanning months to years for relearning fundamental tasks like eating, walking, and speaking. In the United States alone, a staggering 600,000 non-fatal strokes annually result in mild to severe impairments, presenting an urgent need for advanced therapies. The ability to reclaim these vital life skills profoundly enhances a patient’s quality of life and concurrently curtails long-term healthcare expenses. In the current landscape, stroke accounts for a staggering 34% of global healthcare expenditure, underlining the pressing demand for transformative stroke treatments beyond the traditional 24-hour window.
The Impact of Stroke
ConductiveBio is developing advanced therapeutics that promote recovery from stroke, the leading cause of death and disability worldwide. Currently, no medical therapies are available to treat stroke beyond the first 24 hours, leaving most patients without viable treatment options.
This innovative stroke therapy offers the promise of extended treatment windows, revolutionizing stroke care by providing critical interventions beyond the current 24-hour timeframe, potentially enhancing recovery outcomes for a broader range of patients.
We are developing a treatment option for subacute stroke, available to patients in the weeks to months post stroke.
Pre-Clinical Results
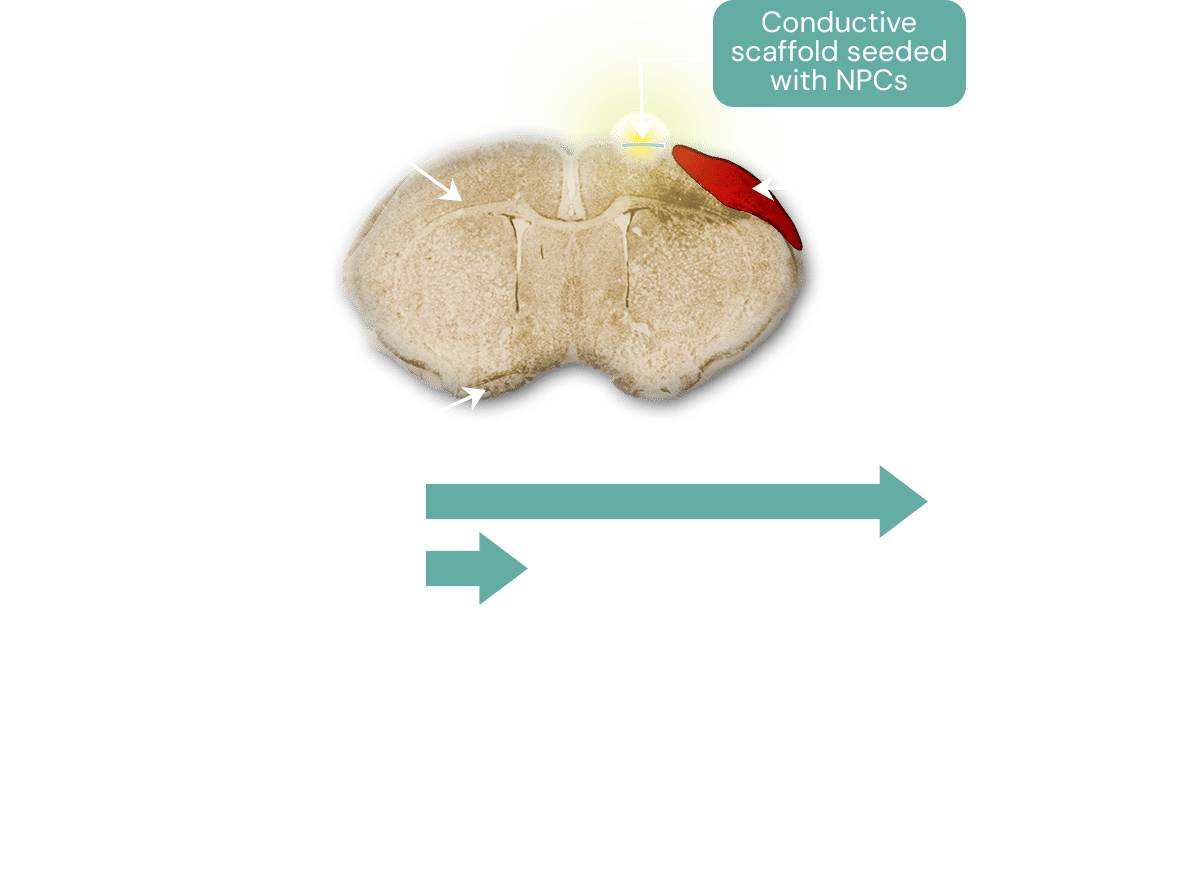
We have completed a highly successful pilot pre-clinical study, conducted with an early product prototype, utilizing an established animal stroke model. In this study, our implant was administered to the treatment group a week after stroke was induced, and standard neurological assessments were used to track recovery over time.
The treatment group achieved 75% functional recovery within 6 weeks based on standard neurological tests, while minimal recovery was observed in the control group.
These exciting pre-clinical results demonstrate the unique promise of this therapy to provide an extended treatment window for stroke.
Nerve Repair
ConductiveBio is tackling peripheral nerve damage, a chronic and painful trauma that affects millions of patients each year worldwide. Accident trauma accounts for 70% of all cases in the US, with >700,000 surgical nerve repairs performed each year. Current treatment options for repairing larger nerve gaps require either complex surgeries involving harvesting graft tissue from the patient’s own body or using cadaver tissue, both of which have significant and unacceptable performance shortfalls.
ConductiveBio is developing electrically conductive implants designed to bridge a nerve gap to promote healing. We are striving to provide a safer, single surgery repair for large gap nerve injuries, targeting the performance of autografts.
We have completed multiple pre-clinical studies for the repair of large nerve gaps in rodent models using prototype implants based on our core technology.
Functional outcomes were greatly improved with our implants, with performance equivalent to “gold standard” autologous grafts for several key indicators without the need for donor site surgery.
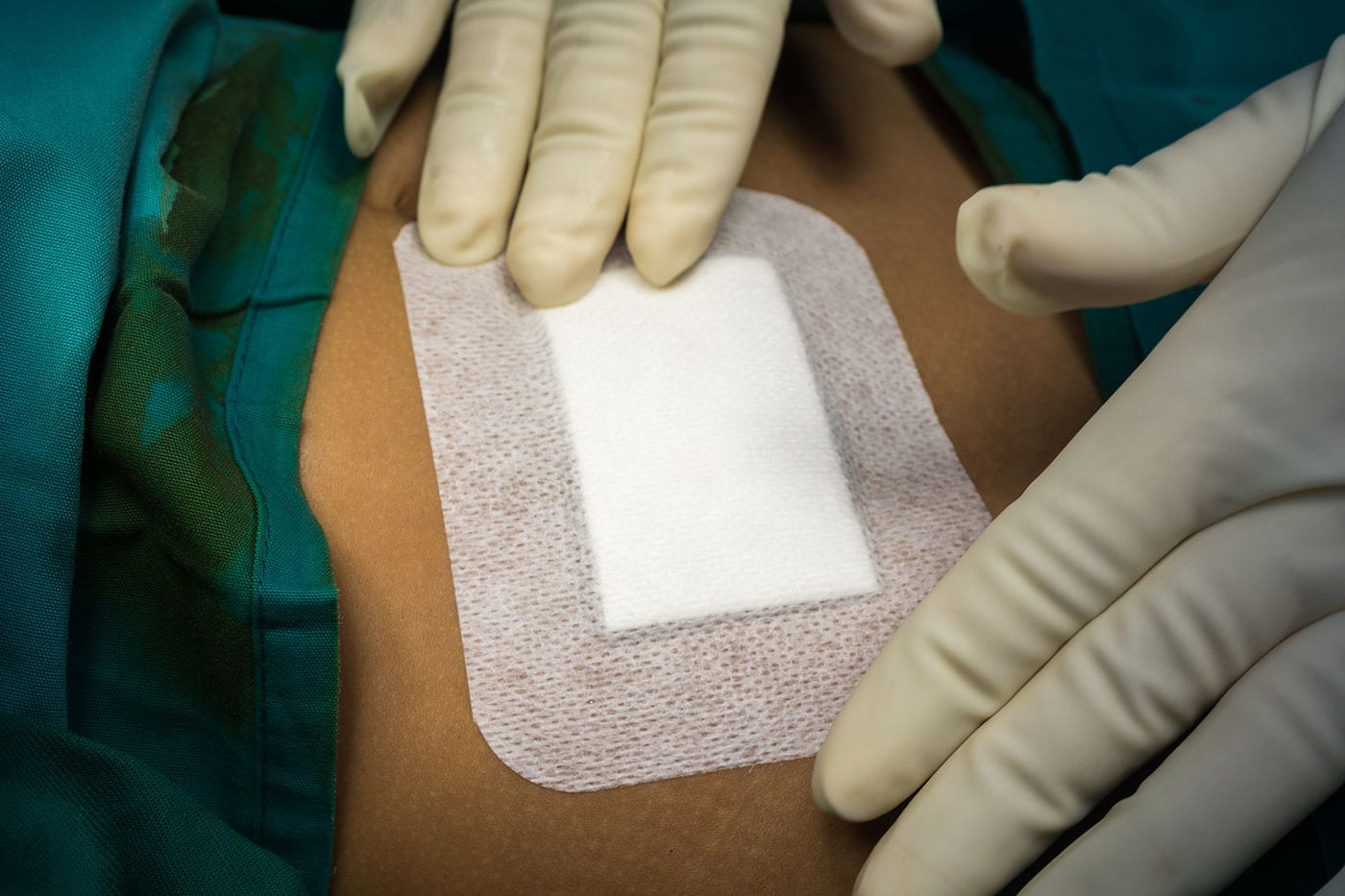
Full-thickness wounds can result from various factors, such as traumatic accidents, burns, pressure ulcers, or specific medical conditions. These wounds are particularly severe as they extend through both the epidermis and the dermis, reaching the subcutaneous tissue beneath. As a natural part of the body’s healing process, an “injury current” is established between the damaged and healthy tissue kickstarting the healing journey.
Leveraging our innovative conductive bioscaffolding technology, we have developed advanced bandage prototypes that enhance the body’s electrical response to injury, creating an ideal environment for tissue repair. Our advanced wound care bandages are meticulously designed to prepare the wound bed for grafting, and we’ve already seen promising initial results from our application of these advanced bandage prototypes in a pilot study involving large animals with full-thickness wounds.